FLOATING OFFSHORE WIND POWER
FLOATING OFFSHORE WIND POWER
UNLOCKS THE STRONG WINDS FAR OUT AT SEA
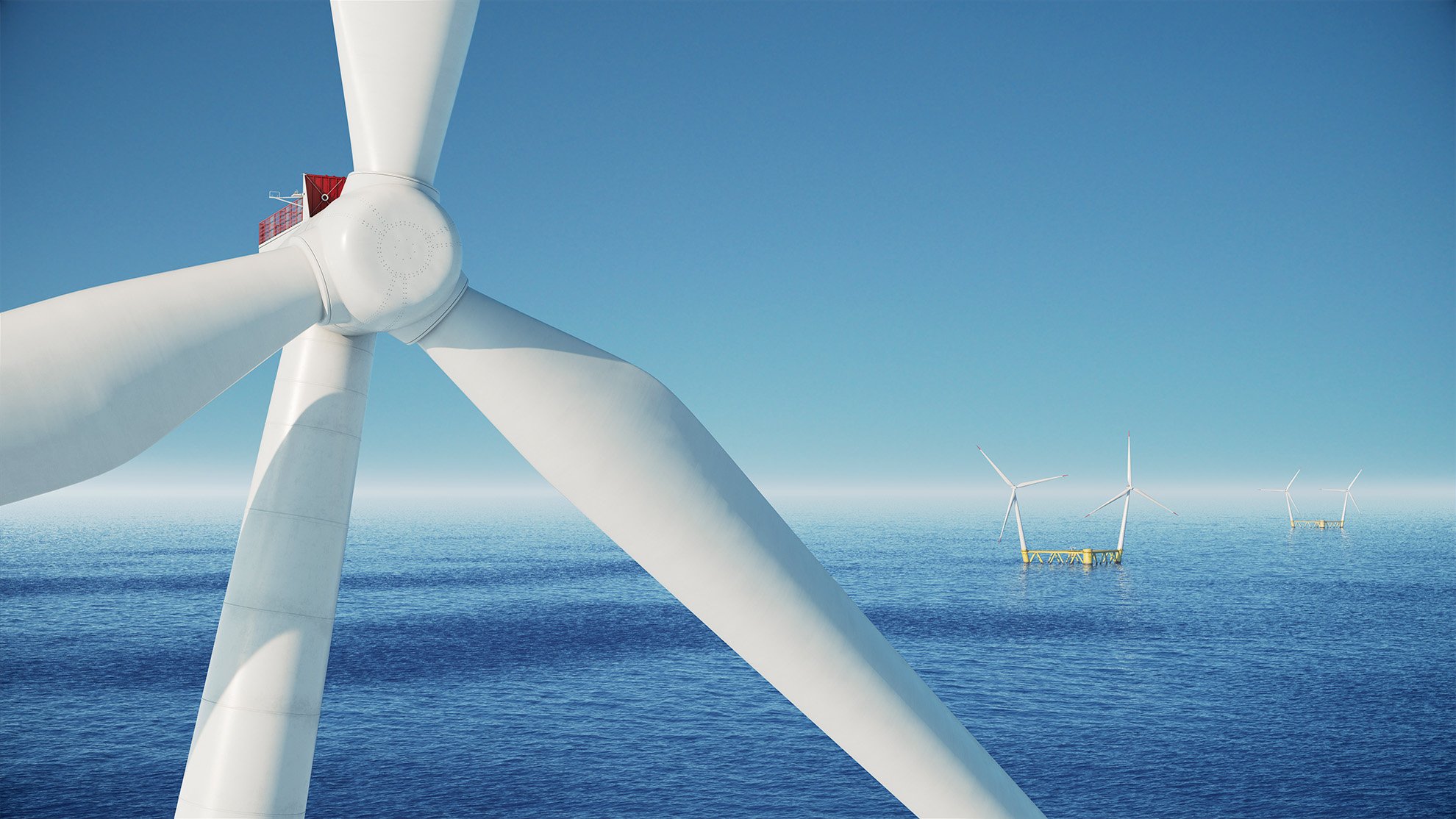
At Hexicon, we believe the sea holds the key to a sustainable energy future. There is an abundance of strong and consistent winds far out at sea where the waters are deep. Floating offshore wind power can access these winds that lie far beyond the reach of traditional bottom-fixed wind turbines, offering a groundbreaking solution for boosting renewable energy generation around the globe.
WHAT IS FLOATING OFFSHORE WIND AND WHY DO WE NEED IT?
Floating offshore wind power is the third generation of wind power technologies. First came land-based wind power, then offshore bottom-fixed wind power, and now, we have floating offshore wind power. Why? Because floating offshore wind power is developed to be flexible. Flexible in site selection, in maintenance, installations, and flexible in adapting to the other stakeholders at sea and the environment.
-
FLEXIBLE SITE SELECTION
Bottom-fixed wind power has today become a crucial part of the energy mix, but it can only be installed in waters with a maximum depth of 60 meters and is restricted to certain seabed conditions. That reality leaves a lot of untapped energy in the deeper waters where the winds are stronger. Floating wind power offers a technology that can be installed in deeper waters where different mooring techniques enable it to be placed in areas with tricky seabed conditions. This means that the wind turbines can access stronger and more consistent ocean winds enabling them to generate more electricity per turbine. Placing turbines in locations with optimal wind conditions thus enhances energy production efficiency, resulting in a more reliable energy source.
FLEXIBLE INSTALLATIONS AND MAINTENCE
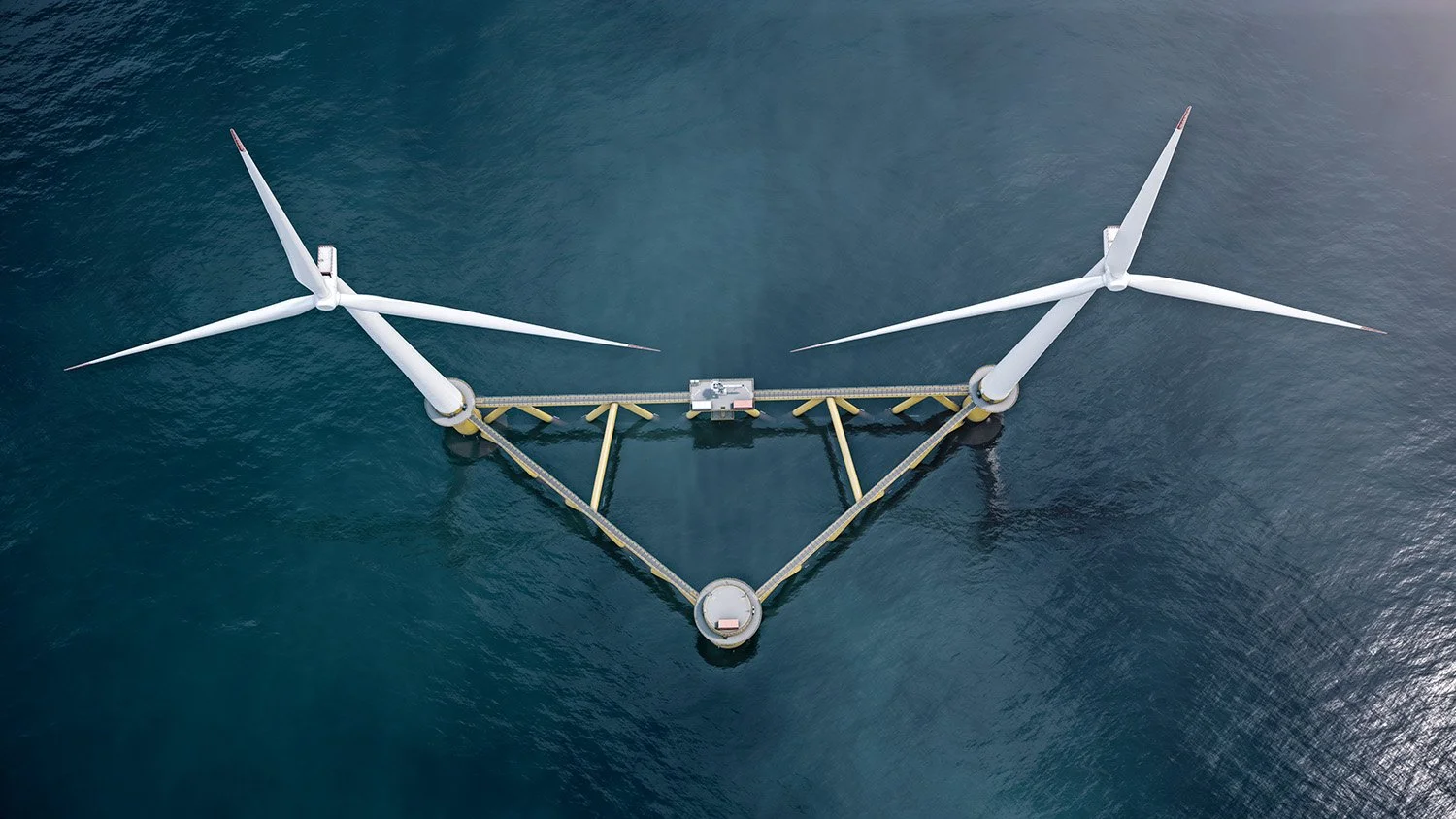
Floating offshore wind is flexible in both installation and maintenance, offering several key advantages over traditional bottom-fixed turbines. One major benefit is that floating platforms can be fully assembled at ports, including the installation of the turbines. Once ready, the platforms are towed to the offshore site using tugboats. This method significantly reduces the complexity and costs associated with installation and eliminates the need for invasive seabed preparations.
In terms of maintenance, floating turbines can be detached from their moorings and towed back to shore for major repairs or upgrades. The flexibility to conduct both installation and maintenance onshore helps lower operational risks, and costs, and improves safety.
FLEXIBILITY FOR STAKEHOLDER CONCERNS AND ENVIRONMENTAL IMPACTS
The flexibility of site selection not only makes floating offshore wind power good at harnessing stronger and consistent winds, it also offers adaptability with stakeholders. Being further out at sea often means that the floating wind power platforms will be beyond the horizon and thus less visible from shore, decreasing the impact on the visual and audible environment on land. Furthermore, sites can be selected based on where they will have a less negative impact on fishing, shipping, military activities, marine reserves and leisure activities. We can also take consideration to avian animals and other marine life by selecting areas that do not conflict with their activities. As research has shown that several marine speciec flourish in offshore wind farm areas, we can e.g. choose areas that needs to recover from excessive fishing from trawling.
Overall, Floating wind power is good for the environment in more than one way, not only does it generate renewable energy that helps us decrease carbon dioxide emissions, it can also coexist with marine life and even have positive effects on the ecosystem.
ACCESSING STRONG WINDS = MORE ENERGY
80% of the best wind resources can be found in deep water areas. There, the winds are stronger and more consistent, and the only way of accessing their energy - is with floating wind power platforms.
OUT OF SIGHT AND SOUND FROM LAND
With floating offshore wind, we do not have to consider water depths, which enable wind farms to be placed further out at sea – beyond the horizon, making them less visible and audible from land.
POSITIVE IMPACT ON THE ENVIRONMENT
Floating wind power benefits the environment by generating renewable energy that reduces carbon emissions and by succesfully coexsiting with marine life, and potentially with a positive impact on its ecosystem.
FLOATING OFFSHORE WIND AND SUSTAINABILITY
Floating offshore wind power can play a pivotal role in the sustainable energy transition, supporting ecological preservation, energy security, and socioeconomic development in coastal regions across the world.
-
ENHANCING MARINE BIODIVERSITY WITH ARTIFICAL REEFS
Research on bottom-fixed offshore wind farms has highlighted several ecological benefits, suggesting that floating wind platforms could offer similar, and potentially greater, advantages for marine ecosystems. Such studies have for instance shown that offshore wind foundations can act as artificial reefs, creating habitats that attract diverse marine species. These structures provide shelter and protection, helping to promote biodiversity in areas where natural reefs may not exist.MINIMISED SEABED DISRUPTION
A key ecological advantage of floating wind platforms is that they avoid the need for invasive pile driving or drilling, which are often required for bottom-fixed platforms. These techniques, used to anchor bottom-fixed platforms into the seabed, create high-frequency vibrations and noise that can disturb marine mammals like dolphins and whales. Floating platforms, on the other hand, are typically secured with mooring lines or gravity-based anchors, minimising seabed disruption and reducing the impact on sensitive marine environments.MARINE PROTECTED AREAS AND SUSTAINABLE FISHING
Moreover, offshore wind farms can serve as marine protected areas, restricting fishing evasive activities like trawling. This limitation on trawling transforms the wind farm zones into safe havens for fish populations. As a result, these areas can become nurseries that help support larger and healthier fish stocks, contributing to more sustainable fishing practices in nearby waters.The floating wind farm areas can also be leveraged by the fish farming industry, where fish cages can be placed between the floating wind platforms to serve as protected areas. Hexicons joint venture, Freja Offshore, and the Norwegian company Subfarm have started a collaboration to explore the opportunities for co-existence within the Mareld project’s sea area outside Sweden's west coast. A new development project will take a closer look at how electricity production and fisheries can be combined. Click for more info.
Sources: UNECE, 2022 & Bonou et al., 2016
-
SOLVES THE GROWING DEMAND FOR MORE ENERGY PRODUCTION
Floating offshore wind power is crucial as global energy demand continues to rise, driven by population growth, urbanisation, and increasing electrification. To meet this growing demand sustainably, integrating more energy into the grid is essential.CRUCIAL FOR MEETING GLOBAL RENEWABLE ENERGY TARGETS
The International Energy Agency (IEA) estimates that the world needs to install around 7,400 GW of renewable energy capacity by 2030 to stay on track for limiting global temperature rise to 1.5°C, in line with climate goals. Offshore wind, including floating platforms, is expected to play a significant role in this transition. Floating offshore wind alone could contribute up to 10% of the total offshore wind capacity by 2030, with projections of around 15-20 GW of floating wind power installed globally by that time.ENCHANSES GRID STABILITY AND FLEXIBILITY
Moreover, as floating offshore wind farms can be installed in deeper waters where wind speeds are stronger and more consistent than land-based or shallow water (bottom-fixed) turbines, they offer a consistent wind resource that allows for more predictable energy production, which is beneficial for grid stability.Additionally, like other wind power technologies, Floating offshore wind power enhances grid flexibility by offering a reliable, adjustable energy source that complements other clean energy options, such as nuclear and solar power. While nuclear plants are designed to operate most efficiently at a constant output, they are less responsive to quick changes in grid demand. Similarly, solar power only generates energy during daylight hours. In contrast, wind power can be scaled up or down based on grid needs, allowing operators to adjust output rapidly. Additionally, wind patterns are often stronger at night when solar energy is unavailable, providing a balanced energy supply throughout the day.
-
JOB CREATION AND ECONOMIC OPPORTUNITIES
Floating offshore wind power has significant potential for contributing to sustainable socioeconomic growth. It can drive job creation in various sectors, including engineering, construction, maintenance, and maritime operations. For instance, the installation, operation, and maintenance of floating wind farms create opportunities for both local and global labor markets.REVITALISING COMMUNITIES AND TRADITIONAL INDUSTRIES
In regions with high unemployment or declining traditional industries, such as shipbuilding or oil extraction, floating offshore wind can help revitalise communities by transitioning them to the green economy.STIMULATING INDUSTRIAL GROWTH AND SUPPLY CHAINS
In terms of industrial growth, floating wind farms stimulate demand for materials like steel, cables, and turbines, supporting supply chains and local industries. They also attract investment in ports, infrastructure, and technology development, boosting economic activity in coastal regions.STAKEHOLDER ENGAGEMENT AND COLLABORATIVE DEVELOPMENT
From a stakeholder management perspective, floating offshore wind offers an opportunity for governments, businesses, and communities to collaborate in achieving energy security and sustainability goals. Proper engagement with stakeholders, including fishermen, environmental groups, and local authorities, ensures that projects not only meet energy demands but also align with broader social and environmental objectives.ENHANCING ECONOMIC RESILIENCE AND ENERGY INDEPENDENCE
On a national and regional level, floating offshore wind can enhance economic resilience by diversifying energy sources and reducing reliance on imported fossil fuels. This strengthens countries' energy independence and contributes to global efforts to mitigate climate change, while also fostering long-term economic growth in key regions.
MORE FACTS ABOUT FLOATING OFFSHORE WIND POWER
As global energy demands rise, renewable energy sources are urgently needed to help meet climate goals, including those set by the Paris Agreement. Floating offshore wind power has matured in global markets, making it a viable solution for scaling up renewable energy production. Several countries are actively implementing policies and support mechanisms to accelerate the development of floating wind projects.
ENERGY GENERATION POTENTIAL
With global energy demand projected to double by 2050, renewable sources like floating offshore wind (FOW) will be essential. The International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA) projects that 90% of the world's electricity could be generated by renewables by 2050. FOW has the potential to significantly expand global wind energy capacity by accessing stronger, more consistent winds in deeper waters, providing a reliable energy source while reducing reliance on fossil fuels. Its ability to complement other renewable sources like solar ensures continuous energy production even during periods of low sunlight or variable wind conditions. According to DNV, FOW could come to account for about 15% of total offshore wind energy by 2050, underscoring its importance in the global energy mix.
COST AND EFFICIANCY
The costs associated with floating offshore wind are expected to decrease significantly over the next decade. Savings can be made throughout the supply chain by achieving economies of scale for the floaters. Innovations in mooring systems, installation techniques, and maintenance processes will contribute to lower operational costs, making FOW a competitive option for clean energy generation.
JOB CREATION AND INDUSTRIAL GROWTH
FOW has significant potential to drive job creation and industrial growth, especially in regions transitioning from coal and other fossil fuels. According to the Global Wind Energy Council (GWEC), the wind industry is expected to create 3.3 million new jobs over the next five years, with a significant portion coming from offshore wind, including floating wind projects. These jobs span various sectors such as project development, manufacturing, installation, operation, and maintenance. As countries invest in offshore wind, especially floating platforms that can be deployed in deeper waters, they will generate opportunities across supply chains and local industries.
For more in-depth information, explore the reports linked below.